TCP Transport Session Management <-
The image below shows a simplified relationship between the primary TCP transport network options.
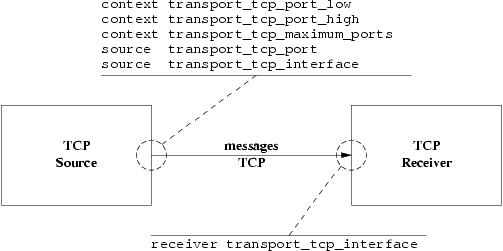
When a source is created, the application can explicitly map it to a transport session by setting the transport_tcp_port (source) option. If a previous source was created on the same context with the same port number, this new source will be mapped to the same transport session. However, two different contexts on the same host may not share the same port number. If a source is created with a port number that is already in use, UM will return an error.
Alternatively, if the application does not explicitly specify a source port, UM will implicitly assign the new source to the default pool of transport sessions defined when the context was created. The pool is defined as a range of port numbers specified by the options transport_tcp_port_low (context) and transport_tcp_port_high (context). In addition, the option transport_tcp_maximum_ports (context) defines the number of transport sessions in the pool.
When a new source is created and the source port is not explicitly defined, UM will check to see how many transport sessions are currently active from the pool within the context. If it is less than transport_tcp_maximum_ports (context) then UM will attempt to use the next port in the range transport_tcp_port_low (context) to transport_tcp_port_high (context). If that port is already in use, UM continues along the range until it finds an unused port, then it uses that port to create the transport session. However, if the context already has activated all transport sessions in the pool, then the new topic is mapped to one of the existing transport sessions, in round-robin fashion.
Note that if you intend to do both explicit mapping and implicit mapping to the default pool of transport sessions, the TCP transport behaves differently than some of the other transport types (e.g. LBT-RM). Any explicitly given port will be added to the default pool. This means that subsequent implicit mappings to the default pool can include this newly added port.
Notice that the default range of ports, 14371 to 14390, is 30 ports. But the default number of transport sessions in the pool is 10. This allows three contexts to be created on the same host and use the same configuration. If more than 3 contexts are intended to co-exist on the same host, the port range and number of transport session per context must be managed to give a unique port number to every transport session.
The option transport_tcp_interface (source) may be used on TCP sources to choose particular interface, overriding the default INADDR_ANY which accepts connections on all interfaces. Similarly, transport_tcp_interface (receiver) may be used on receivers to choose a particular interface.
Reference <-
transport_tcp_interface (receiver) <-
- Specifies the network interface to which UM receivers bind before connecting to sources.
- You can specify the full IP address of interface, or just the network part (see Specifying Interfaces for details).
- Default is set to default_interface (context), if specified.
- Note: if specifying an interface name in an XML-format file, see Interface Device Names and XML.
Scope: receiver Type: lbm_ipv4_address_mask_t Default value: 0.0.0.0 (INADDR_ANY)
When to Set: Can only be set during object initialization.
transport_tcp_interface (source) <-
- Specifies the network interface over which UM accepts connection requests (from topic receivers).
- You can specify the full IP address of interface, or just the network part (see Specifying Interfaces for details).
- Default is set to default_interface (context), if specified. Otherwise, it is set to INADDR_ANY, meaning that it will not bind to a specific interface. You can also set this option to 0.0.0.0/0 which produces the same result.
- Be aware that this option is applied to the transport session when the first topic is created on that session. Thus, setting a different interface for a subsequent topic that maps onto the same transport session will have no effect.
- Note: if specifying an interface name in an XML-format file, see Interface Device Names and XML.
Scope: source Type: lbm_ipv4_address_mask_t Default value: 0.0.0.0 (INADDR_ANY)
When to Set: Can only be set during object initialization.
transport_tcp_maximum_ports (context) <-
- Maximum size of TCP source transport session default pool.
- See TCP Transport Session Management for how TCP source transport sessions are managed.
Scope: context Type: lbm_uint16_t Units: number of ports Default value: 10 When to Set: Can only be set during object initialization.
transport_tcp_port (source) <-
- The TCP port to be used for the source transport session.
- Setting this option to non-zero overrides the use of the default pool of TCP source transport sessions.
- The UM source listens on this port. Receivers that join the source's transport session connect to this port, and the source sends message data across that connection.
- See TCP Transport Session Management for how TCP source transport sessions are managed.
- See Port Assignments for more information about configuring ports.
- Note that this port is only used by TCP sources. Receiver port numbers are taken from the host's Ephemeral Ports and are not configurable.
- Attention
- If a source is configured for a port that is not currently part of the transport session default pool, UM will create a new transport session for this port and add it to the default pool. See Transport Session Differences.
Scope: source Type: lbm_uint16_t Default value: 0 (pick open port) Byte order: Network When to Set: Can only be set during object initialization.
transport_tcp_port_high (context) <-
- High TCP port number of range for the default pool of TCP source transport sessions.
- When transport_tcp_port (source) is not specified, a newly-created transport session will use an unused port from this range. The UM source listens on this port. Receivers that join the source's transport session connect to this port, and the source sends message data across that connection.
- See also transport_tcp_port_high (context).
- See TCP Transport Session Management for how TCP source transport sessions are managed.
- See Port Assignments for more information about configuring ports.
- Note that this range of ports is only used by TCP sources. Receiver port numbers are taken from the host's Ephemeral Ports and are not configurable.
Scope: context Type: lbm_uint16_t Default value: 14390 Byte order: Host When to Set: Can only be set during object initialization.
transport_tcp_port_low (context) <-
- Low TCP port number of range for the default pool of TCP source transport sessions.
- When transport_tcp_port (source) is not specified, a newly-created transport session will use an unused port from this range. The UM source listens on this port. Receivers that join the source's transport session connect to this port, and the source sends message data across that connection.
- See also transport_tcp_port_high (context).
- See TCP Transport Session Management for how TCP source transport sessions are managed.
- See Port Assignments for more information about configuring ports.
- Note that this range of ports is only used by TCP sources. Receiver port numbers are taken from the host's Ephemeral Ports and are not configurable.
Scope: context Type: lbm_uint16_t Default value: 14371 Byte order: Host When to Set: Can only be set during object initialization.